You are given a positive integer n representing n cities numbered from 1 to n. You are also given a 2D array roads where roads[i] = [ai, bi, distancei] indicates that there is a bidirectional road between cities ai and bi with a distance equal to distancei. The cities graph is not necessarily connected.
The score of a path between two cities is defined as the minimum distance of a road in this path.
Return the minimum possible score of a path between cities 1 and n.
Note:
- A path is a sequence of roads between two cities.
- It is allowed for a path to contain the same road multiple times, and you can visit cities
1andnmultiple times along the path. - The test cases are generated such that there is at least one path between
1andn.
Example
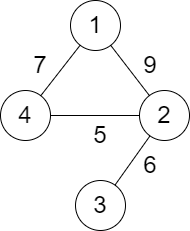
Input: n = 4, roads = [[1,2,9],[2,3,6],[2,4,5],[1,4,7]]
Output: 5
Explanation: The path from city 1 to 4 with the minimum score is: 1 -> 2 -> 4. The score of this path is min(9,5) = 5.
It can be shown that no other path has less score.
Solution
Great solution here
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} roads
* @return {number}
*/
var minScore = function (n, roads) {
//create a graph
const graph = new Array(n + 1).fill().map(() => []);
//create a set to keep track of visited nodes
const visited = new Set([]);
//add the roads to the graph
for (const [v1, v2, distance] of roads) {
//add the distance to the graph
graph[v1].push([v2, distance]);
//add the distance to the graph
graph[v2].push([v1, distance]);
}
//start at node 1
const queue = [1];
//add node 1 to the visited set
visited.add(1);
let ans = Infinity;
while (queue.length > 0) {
//remove the first node from the queue
const node = queue.shift();
// For each neighbor of the current node
for (const [next, distance] of graph[node]) {
//if the next node is the last node, return the answer
ans = Math.min(ans, distance);
//if the next node is the last node, return the answer
if (visited.has(next)) continue;
//add the next node to the visited set
visited.add(next);
//add the next node to the queue
queue.push(next);
}
}
return ans;
};