There are n computers numbered from 0 to n - 1 connected by ethernet cables connections forming a network where connections[i] = [ai, bi] represents a connection between computers ai and bi. Any computer can reach any other computer directly or indirectly through the network.
You are given an initial computer network connections. You can extract certain cables between two directly connected computers, and place them between any pair of disconnected computers to make them directly connected.
Return the minimum number of times you need to do this in order to make all the computers connected. If it is not possible, return -1.
Example
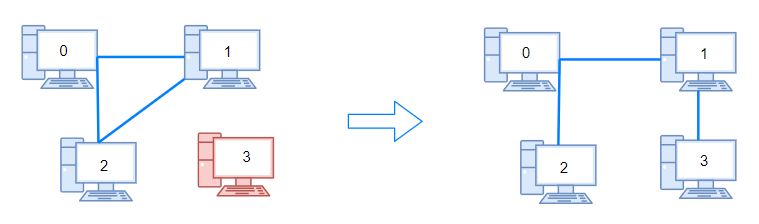
Input: n = 4, connections = [[0,1],[0,2],[1,2]]
Output: 1
Explanation: Remove cable between computer 1 and 2 and place between computers 1 and 3.
Solution
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} connections
* @return {number}
*/
var makeConnected = function (n, connections) {
//if the number of connections is less than n-1, return -1
if (connections.length < n - 1) return -1;
//create a graph
const graph = new Array(n).fill().map(() => []);
//create a set to keep track of visited nodes
const visited = new Set([]);
//add the connections to the graph
for (const [v1, v2] of connections) {
//add the connection to the graph
graph[v1].push(v2);
//add the connection to the graph
graph[v2].push(v1);
}
//start at node 0
const queue = [0];
//add node 0 to the visited set
visited.add(0);
let ans = 0;
//while the queue is not empty
while (queue.length > 0) {
//get the current node
const node = queue.shift();
//loop through the neighbors
for (const neighbor of graph[node]) {
//if the neighbor is not visited
if (!visited.has(neighbor)) {
//add the neighbor to the visited set
visited.add(neighbor);
//add the neighbor to the queue
queue.push(neighbor);
}
}
//if the queue is empty
if (queue.length === 0) {
//loop through the graph
for (let i = 0; i < graph.length; i++) {
//if the node is not visited
if (!visited.has(i)) {
//add the node to the visited set
visited.add(i);
//add the node to the queue
queue.push(i);
//increment the answer
ans++;
//break out of the loop
break;
}
}
}
}
return ans;
};