You are given a directed graph of n nodes numbered from 0 to n - 1, where each node has at most one outgoing edge.
The graph is represented with a given 0-indexed array edges of size n, indicating that there is a directed edge from node i to node edges[i]. If there is no outgoing edge from node i, then edges[i] == -1.
Return the length of the longest cycle in the graph. If no cycle exists, return -1.
A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node.
Example
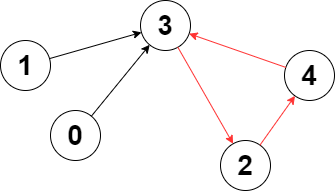
Input: edges = [3,3,4,2,3]
Output: 3
Explanation: The longest cycle in the graph is the cycle: 2 -> 4 -> 3 -> 2.
The length of this cycle is 3, so 3 is returned.
Solution
Good solution found here
const longestCycle = (edges) => {
let n = edges.length,
g = Array(n).fill(-1);
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (edges[i] != -1) g[i] = edges[i];
}
return detectLongestCycleDG(g);
};
// direct parent -> child, no queue
const detectLongestCycleDG = (g) => {
// each node's child <= 1
let n = g.length,
cycleStart = Array(n).fill(-1),
dis = Array(n).fill(Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER),
res = -1;
for (let i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (cycleStart[i] == -1) {
// current node should not under any other cycle, can be as a cycle start node
let cur = i,
step = 0;
while (1) {
if (dis[cur] != Number.MAX_SAFE_INTEGER) {
if (cycleStart[cur] == i) {
// cycle find
res = Math.max(res, step - dis[cur]);
}
break;
}
dis[cur] = step;
cycleStart[cur] = i; // set cycle start node to current node
cur = g[cur];
step++;
}
}
}
return res;
};