Given a reference of a node in a connected undirected graph.
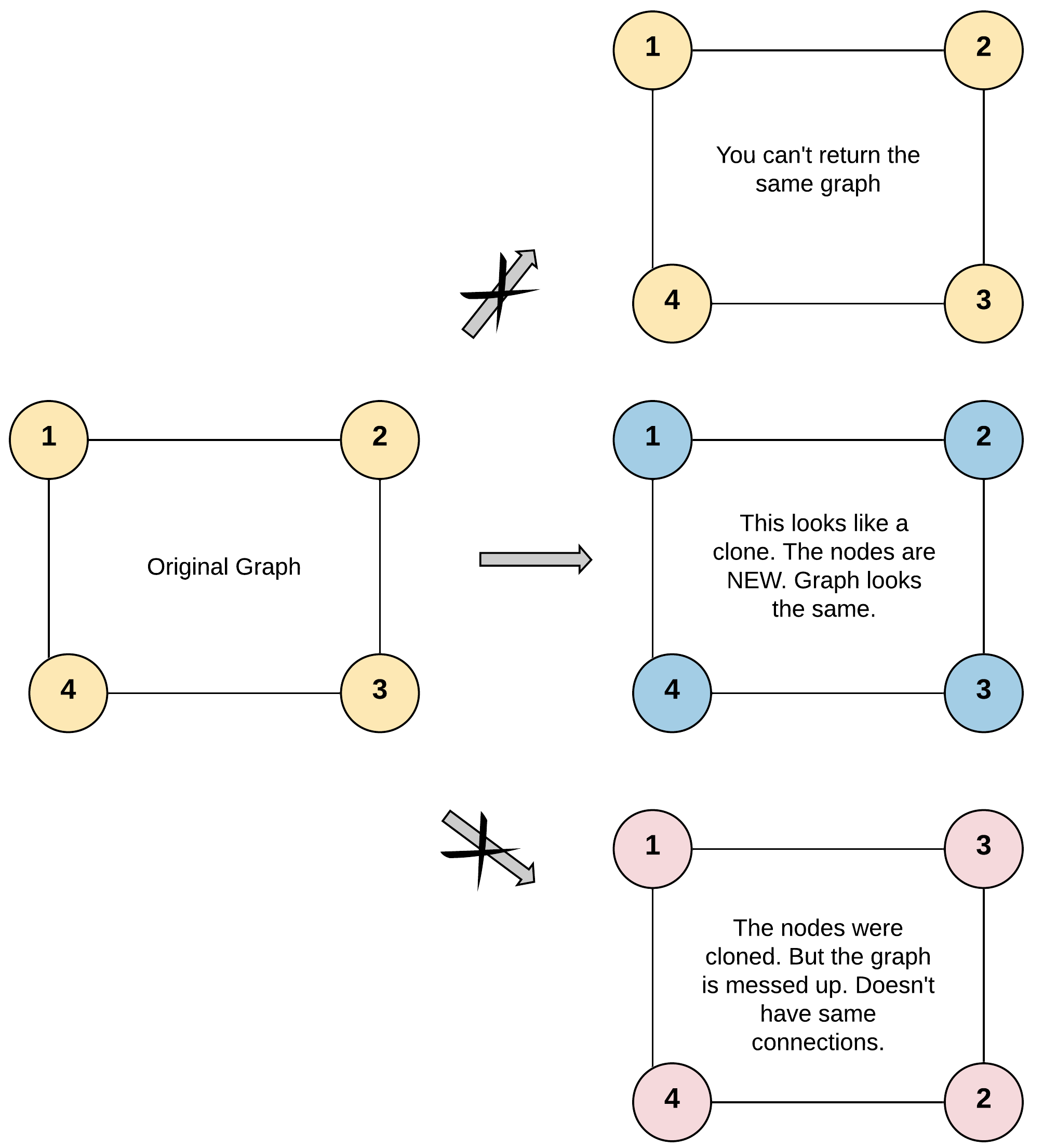
Return a deep copy (clone) of the graph.
Each node in the graph contains a value (int) and a list (List[Node]) of its neighbors.
class Node {
public int val;
public List<Node> neighbors;
}
Test case format:
For simplicity, each node’s value is the same as the node’s index (1-indexed). For example, the first node with val == 1, the second node with val == 2, and so on. The graph is represented in the test case using an adjacency list.
An adjacency list is a collection of unordered lists used to represent a finite graph. Each list describes the set of neighbors of a node in the graph.
The given node will always be the first node with val = 1. You must return the copy of the given node as a reference to the cloned graph.
Example
Input: adjList = [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Output: [[2,4],[1,3],[2,4],[1,3]]
Explanation: There are 4 nodes in the graph.
1st node (val = 1)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
2nd node (val = 2)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
3rd node (val = 3)'s neighbors are 2nd node (val = 2) and 4th node (val = 4).
4th node (val = 4)'s neighbors are 1st node (val = 1) and 3rd node (val = 3).
Solution
I found a helpful solution here.
var cloneGraph = function(node) {
// If start node is null then we can't do any cloning
let start = node;
if (start === null) return null;
// vertexMap is the original node reference to our node
const vertexMap = new Map();
// Add the start node to the queue. Give the start node a clone in the vertex map
const queue = [start]
vertexMap.set(start, new Node(start.val));
/*
* Breadth first search continues until we process all the vertices in the graph
* In the original graph. We know this is done when queue is empty
*/
while (queue.length > 0) {
// We grab a node. We will express all of the edges coming off of this node.
const currentVertex = queue.shift();
// Iterate over all adjacents.
for (const neighbor of currentVertex.neighbors) {
// Has this neighbor been given a clone?
if (!vertexMap.has(neighbor)) {
/*
* No? Give it a mapping and add the original neighbor to the search queue so we
* can express ITS edges later
*/
vertexMap.set(neighbor, new Node(neighbor.val))
queue.push(neighbor);
}
/*
* Draw the edge from currVertex's clone to neighbor's clone. Do you see how our
* hashtable makes this quick access possible?
*/
vertexMap.get(currentVertex).neighbors.push(vertexMap.get(neighbor));
}
}
return vertexMap.get(start);