Given the root of a binary tree, return the maximum width of the given tree.
The maximum width of a tree is the maximum width among all levels.
The width of one level is defined as the length between the end-nodes (the leftmost and rightmost non-null nodes), where the null nodes between the end-nodes that would be present in a complete binary tree extending down to that level are also counted into the length calculation.
It is guaranteed that the answer will in the range of a 32-bit signed integer.
Example
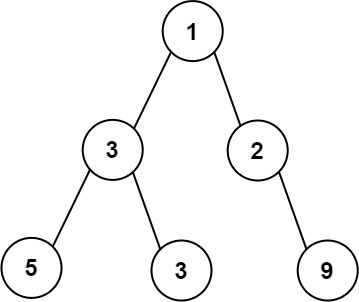
Input: root = [1,3,2,5,3,null,9]
Output: 4
Explanation: The maximum width exists in the third level with length 4 (5,3,null,9).
Solution
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var widthOfBinaryTree = function (root) {
//Set minPos and maxWidth to 0
const minPos = [0];
let maxWidth = 0;
//Call DFS function, then return result
callDFS(root, 0, 0);
return maxWidth;
function callDFS(node, level, pos) {
//If node is null, return
if (!node) return;
//If minPos at level is undefined, set it to pos
if (minPos[level] === undefined) minPos.push(pos);
//Calculate diff between pos and minPos at level
const diff = pos - minPos[level];
//Set maxWidth to max of maxWidth and diff+1
maxWidth = Math.max(maxWidth, diff + 1);
//Call DFS on left and right nodes
callDFS(node.left, level + 1, diff * 2);
//
callDFS(node.right, level + 1, diff * 2 + 1);
}
};