An undirected graph of n nodes is defined by edgeList, where edgeList[i] = [ui, vi, disi] denotes an edge between nodes ui and vi with distance disi. Note that there may be multiple edges between two nodes.
Given an array queries, where queries[j] = [pj, qj, limitj], your task is to determine for each queries[j] whether there is a path between pj and qj such that each edge on the path has a distance strictly less than limitj .
Return a boolean array answer, where answer.length == queries.length and the jth value of answer is true if there is a path for queries[j] is true, and false otherwise.
Example
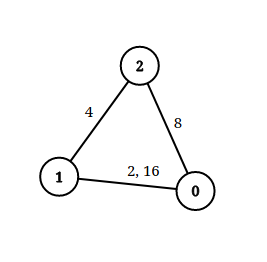
Input: n = 3, edgeList = [[0,1,2],[1,2,4],[2,0,8],[1,0,16]], queries = [[0,1,2],[0,2,5]]
Output: [false,true]
Explanation: The above figure shows the given graph. Note that there are two overlapping edges between 0 and 1 with distances 2 and 16.
For the first query, between 0 and 1 there is no path where each distance is less than 2, thus we return false for this query.
For the second query, there is a path (0 -> 1 -> 2) of two edges with distances less than 5, thus we return true for this query.
Solution
Great solution found here.
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edgeList
* @param {number[][]} queries
* @return {boolean[]}
*/
var distanceLimitedPathsExist = function (n, edgeList, queries) {
// Sort the queries by limit
let index = new Array(n).fill().map((_, i) => i);
// Create an array of indices
let keys = new Array(queries.length).fill().map((_, i) => i);
// Create an array of results
let result = new Array(queries.length),
j = 0;
// Find the index of x
const find = (x) => (x !== index[x] ? (index[x] = find(index[x])) : index[x]);
// Union x and y
const union = (x, y) => (index[find(x)] = find(y));
edgeList.sort((a, b) => a[2] - b[2]);
keys.sort((a, b) => queries[a][2] - queries[b][2]);
for (let i of keys) {
// Destructure the queries
let [a, b, c] = queries[i];
// While the edgeList is less than c, union the edgeList
while (edgeList[j]?.[2] < c) union(edgeList[j][0], edgeList[j++][1]);
// Set the result to the index of a and b
result[i] = find(a) === find(b);
}
return result;
};