Alice and Bob have an undirected graph of n nodes and three types of edges:
- Type 1: Can be traversed by Alice only.
- Type 2: Can be traversed by Bob only.
- Type 3: Can be traversed by both Alice and Bob.
Given an array edges where edges[i] = [typei, ui, vi] represents a bidirectional edge of type typei between nodes ui and vi, find the maximum number of edges you can remove so that after removing the edges, the graph can still be fully traversed by both Alice and Bob. The graph is fully traversed by Alice and Bob if starting from any node, they can reach all other nodes.
Return the maximum number of edges you can remove, or return -1 if Alice and Bob cannot fully traverse the graph.
Example
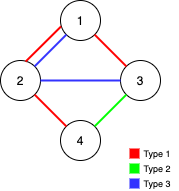
Input: n = 4, edges = [[3,1,2],[3,2,3],[1,1,3],[1,2,4],[1,1,2],[2,3,4]]
Output: 2
Explanation: If we remove the 2 edges [1,1,2] and [1,1,3]. The graph will still be fully traversable by Alice and Bob. Removing any additional edge will not make it so. So the maximum number of edges we can remove is 2.
Solution
Great solution found here.
/**
* @param {number} n
* @param {number[][]} edges
* @return {number}
*/
var maxNumEdgesToRemove = function (n, edges) {
const alice = new UnionFind(n),
bob = new UnionFind(n);
// Count number of times parent changed
let count = 0;
// Check all type 3 edges
for (let [type, u, v] of edges) {
if (type === 3 && alice.union(u, v) && bob.union(u, v)) count++;
}
// Check all type 1 & 2 edges
for (let [type, u, v] of edges) {
if (type === 1 && alice.union(u, v)) count++;
if (type === 2 && bob.union(u, v)) count++;
}
// If groups = 1 then all nodes are connected
if (alice.groups === 1 && bob.groups === 1) return edges.length - count;
else return -1;
};
//////////////// Union Find Data Structure \\\\\\\\\\\\\\\\
class UnionFind {
constructor(n) {
this.parent = new Array(n).fill().map((_, i) => i);
this.groups = n;
}
find(i) {
if (this.parent[i] !== i) this.parent[i] = this.find(this.parent[i]);
return this.parent[i];
}
// Return true if parent is changed
union(i, j) {
const x = this.find(i),
y = this.find(j);
if (x === y) return false;
else {
this.parent[y] = x;
this.groups--;
return true;
}
}
}